In this article, we will discuss the KNN Classification method of analysis.
What is the KNN Classification Algorithm?
The KNN (K Nearest Neighbors) algorithm analyzes all available data points and classifies this data, then classifies new cases based on these established categories. It is useful for recognizing patterns and for estimating. Let’s say we want to determine the likelihood of loan default based on two predictors (age and loan type), with ‘default’ being the target.
We would first determine K = number of nearest neighbors (in terms of distance) to check for class assignment. Then calculate the distance between an instance and all the training instances. Then we would rank the instances by distance and find the nearest neighbors. In other words, we would find the shortest distance from the new instance. After that, we would gather the classes of the nearest neighbors to find the majority. This majority of class is a final predicted value of a class.
Let’s look at an example of KNN Classification, based on two attributes: Acid durability and strength. The goal is to classify a paper tissue into good/bad quality classes.
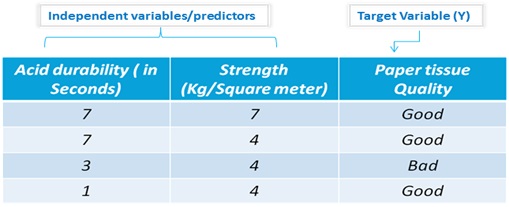
As the majority class = Good for the three nearest neighbors (two out of three records have class = Good), predicted class of an instance = Good, i.e. quality of a paper tissue having acid durability =3 and strength =7 is good.
How Can KNN Classification Help an Enterprise?
KNN Classification analysis can be useful in evaluating many types of data.
- Credit/Loan Approval Analysis – Given a list of client transactional attributes, the business can predict whether a client will default on a bank loan.
- Weather Prediction – Based on temperature, humidity, pressure etc., an organization can predict if it will be rainy/sunny/cold.
- Fraud Analysis – Based on various bills submitted for reimbursement by an employee for food, travel, and other expense a business can predict the likelihood of fraud.
Let’s look at two use cases to illustrate the benefit of KNN Classification.
Use Case – 1
Business Problem: A bank loans officer wants to predict if the loan applicant will be a bank defaulter or non-defaulter based on attributes such as loan amount, monthly installment, employment tenure, the number of times a payment has been delinquent, annual income, debt to income ratio etc. Here, the target variable would be ‘past default status’ and the predicted class would contain the values or ‘yes or no’ representing ‘likely to default/unlikely to default’ class respectively.
Business Benefit: Once classes are assigned, the bank will have a loan applicant dataset with each applicant labeled as “likely/unlikely to default”. Based on these labels, the bank can easily make a decision on whether to give a loan to an applicant and the credit limit and interest rate for each applicant, based on the amount of risk.
Use Case – 2
Business Problem: A doctor wants to predict the likelihood of successful treatment for a new patient based on various attributes such as blood pressure, hemoglobin, blood sugar, the name of a drug given to the patient, the type of treatment given to the patient etc. Here, the target variable would be ‘past cure status’ and the predicted class would contain values ‘yes or no’ meaning ‘prone to cure/ not prone to cure’ respectively.
Business Benefit: Given the health and body profile of a patient and the recent treatments and drugs prescribed for the patient, the doctor can predict the probability and make recommendations on changes in treatment/drugs.
The KNN Classification algorithm is useful in determining probable outcome and results and in forecasting and predicting results, given the existence of multiple variables.
The Smarten approach to augmented analytics and modern business intelligence focuses on the business user and provides tools for Advanced Data Discovery so users can perform early prototyping and test hypotheses without the skills of a data scientist. Smarten Augmented Analytics tools include assisted predictive modeling, smart data visualization, self-serve data preparation, Clickless Analytics with natural language processing (NLP) for search analytics, Auto Insights, Key Influencer Analytics, and SnapShot monitoring and alerts. These tools are designed for business users with average skills and require no specialized knowledge of statistical analysis or support from IT or data scientists. Businesses can advance Citizen Data Scientist initiatives with in-person and online workshops and self-paced eLearning courses designed to introduce users and businesses to the concept, illustrate the benefits and provide introductory training on analytical concepts and the Citizen Data Scientist role.
The Smarten approach to data discovery is designed as an augmented analytics solution to serve business users. Smarten is a representative vendor in multiple Gartner reports including the Gartner Modern BI and Analytics Platform report and the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Business Intelligence and Analytics Platforms Report.










